Introducing
WAGO Compact Electronic Circuit Breakers
The future of DC Circuit protection today.
- Panel Builders can save almost 80% space!
8 channel ECB just 32mm wide, the slimmest on the market
- Can help End Users avoid expensive down time.
Adjustable pre-alarm provides warning of an over current.
- OEMs can achieve compliance to EN 60204.
Thanks to Electronic current measurement, using an ECB can enable predictable tripping to achieve 5 second disconnection under earth fault.

Maximum safety, efficiency and reliability.
WAGO’s ECBs ensure that a fault on one DC circuit is protected whilst ensuring critical automation control equipment, such as a PLC, does not lose power that can result in time consuming re-booting or costly disruption to a process or machine operation.
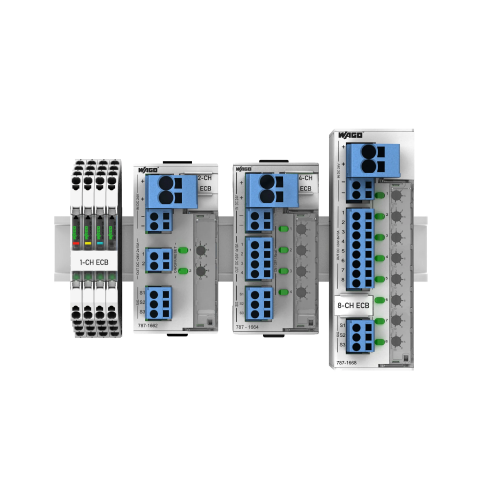
Multi-channel ECBs
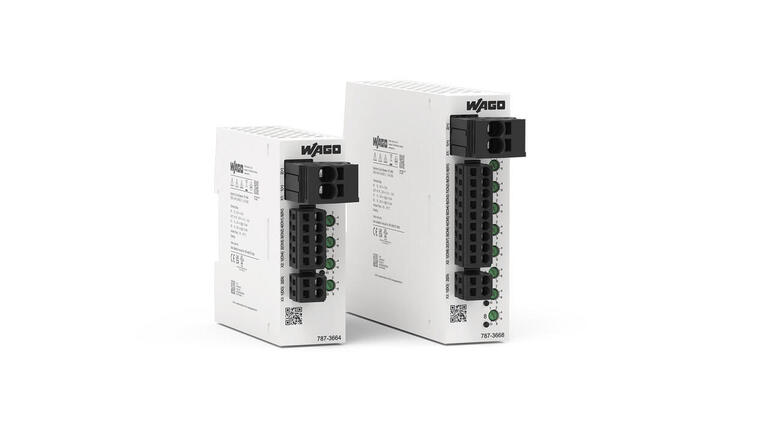

Series 787-366
- Just 32mm wide – smallest on the market
- Overload warning threshold enables preventative maintenance
- Remote monitoring and reset enable easy diagnostics and maintenance
- Removable connections – Push in solid or ferruled cable
- QR Code – Fast access to product information
- Individual channel adjustment – Enables easy setting of current
- Multicolour LEDs green/red/yellow for signalling the operating state of each channel – Easy diagnostics
- 16A rating by parallel operation of 2 channels
Single-channel ECBs

Series 787-3861
- Push-in’ connections – fast, reliable connections
- Just 6mm width – saves panel space
- Multicolour LEDs green/red/yellow for signalling the operating state of each channel – Easy diagnostics
- Potential distribution modules – enables easy wiring and modular solution
- Jumper bars slot for every terminal – Easily combine ECBs to create a modular array
- *NEC Class 2 versions available US markets (<100W 24Vdc)
ECB Advantages
- Switch off secondary-side overcurrents and short circuits – even with long cable runs and small conductor cross-sections – precisely, quickly and repeatedly
- Selectivity
- Remote operation via digital input and output
- Readout functions (communication) through serial data transfer via digital input and output
- Advantageous installation size and width, for example, eight output channels in just 32 mm that saves almost 80% of installation space compared to miniature circuit breakers
- Adjustable current assignable for each channel
- Satisfy EN 60204-1 requirements for dependably switching off ground faults after five seconds
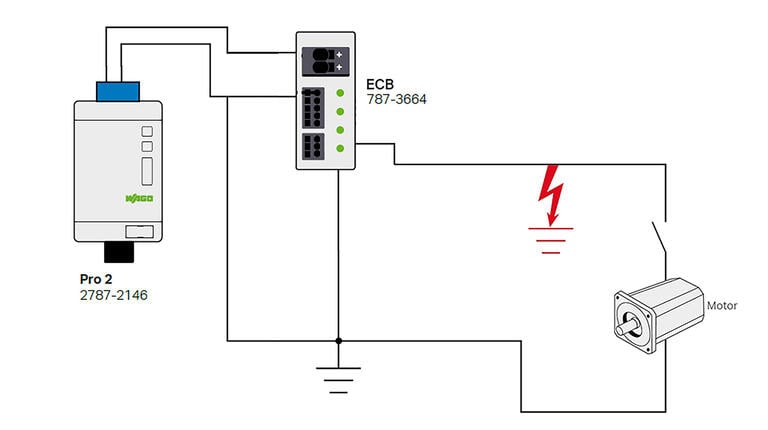
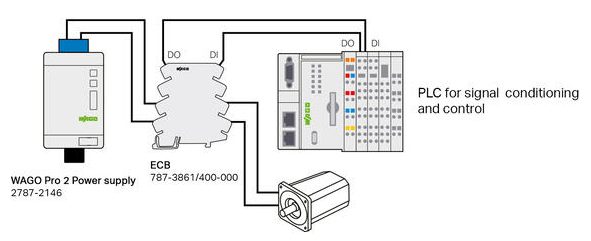
Application Example
Ensuring that a fault on one DC circuit is protected, WAGO ECBs also ensures that critical automation control equipment, such as a PLC, does not lose power that can result in time consuming re-booting or costly disruption to a process or machine operation.
In the example shown, if a motor overload on channel 1 occurs, with the correct use of a WAGO ECB ensures only that channel is switched off, the PLC on channel 4 is unaffected ensuring overall control is retained.
Furthermore, using the WAGO Compact ECB; 787-3664 with the overload ‘pre-alarm’ configured, it may even be possible to avoid a trip completely by implementing this valuable ‘condition-monitoring benefit:
- Pro 2 10A 24V dc 2787-2146
- WAGO ECB with 4 output channels
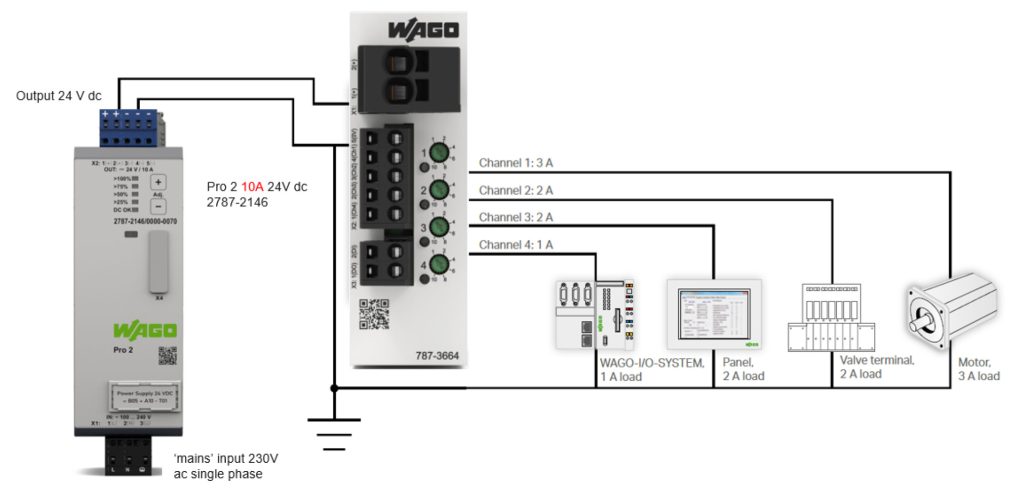
Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
Electronic protection | Enables accurate, predictable tripping ensuring fast protection of system |
Overcurrent pre-alarm
| Allows predictive / planned maintenance |
Remote monitoring | Allows monitoring of status |
Extremely compact
| Saves almost 80% panel space (Typical MCB is 18mm wide compared to 32mm 8 channel WAGO ECB) |
Remotely monitored, controllable and resettable
| Saves almost 80% panel space (Typical MCB is 18mm wide compared to 32mm 8 channel WAGO ECB)
|
Compared to fuse, resettable | No spare fuses required
|
Allows compliance to BS EN 60204 (Safety of Machinery) | Can help ensure ground faults in control circuits are switched off within 5 seconds |
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Why secondary-side fuse protection?
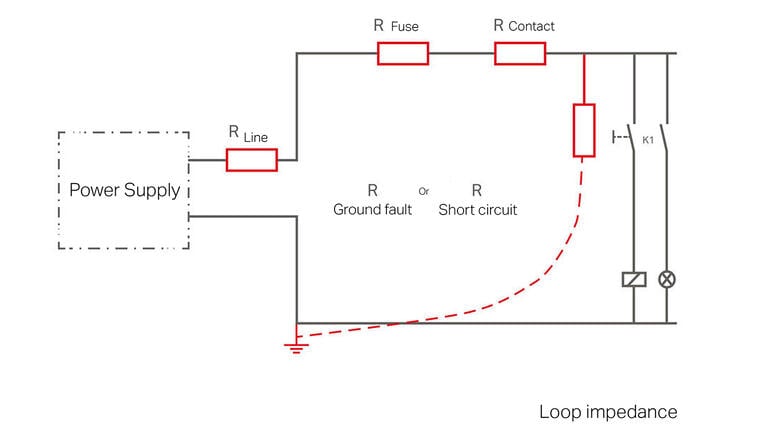
On the secondary side, switched-mode power supplies provide DC voltage to control circuit loads (e.g., controllers, operating panels, displays and auxiliary relays). These control circuits also call for wiring protection and if the load has no protective unit of its own, device protection as well. Furthermore, Machinery Directive EN 60204 requires the detection of hazardous ground faults in control circuits and switching off within five seconds.
The overcurrent protection in primary switched-mode power supplies reacts very quickly to overcurrents on the output side. Selective protection of individual current paths in the secondary circuit via fuses or conventional circuit breakers is often ineffective if the power supply cannot deliver a brief overcurrent.
What types of fuse protection are there?
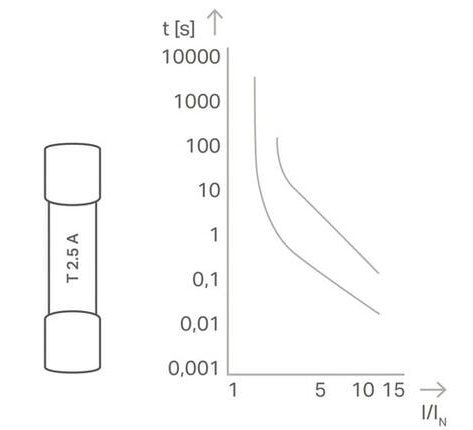
Thermal
Possible applications:
- Low-voltage, high-power and DP fuses
High overcurrents required for fast tripping
Explanation:
- In the example: ten-fold overcurrent (related to fuse nominal current): tripping within the range 30 ms (best case) or 200 ms (worst case)
- Only two-fold overcurrent: tripping within the range 2 s (best case) or >100 s (worst case)
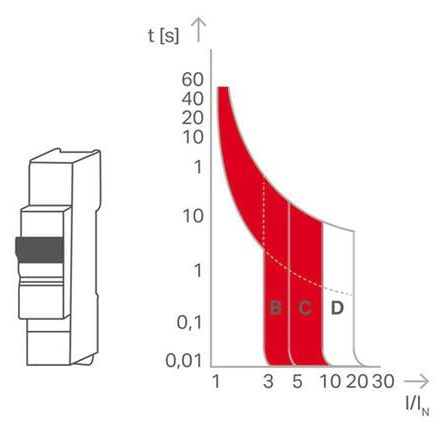
Thermal and magnetic
Possible applications:
- Found in circuit breakers or motor protection switches
- High overcurrents required for fast tripping
Explanation:
- In the example: three- to five-fold overcurrent for B-characteristic and AC operation, additional safety factor 1.2 or 1.5
- Thus, in the worst case scenario, a tripping current of 7.5 times the nominal current is necessary.
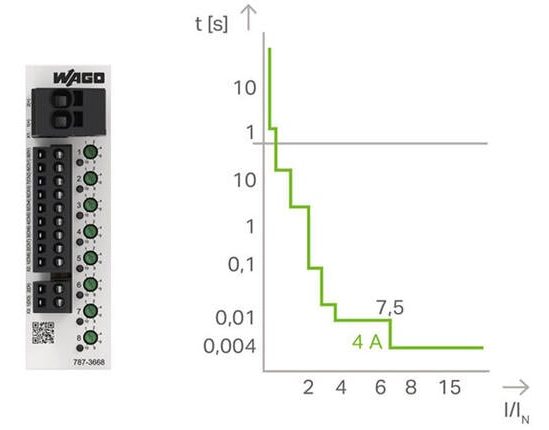
Electronic
Functions of a WAGO ECBs:
- Ensure precision settings
- Reaction within a short time – even at low overcurrents
- Protection of long cable runs and small cross sections possible
Explanation:
WAGO ECBs ensure reliable protection, even at low overcurrents and with long cable lengths.
How does an ECB function?
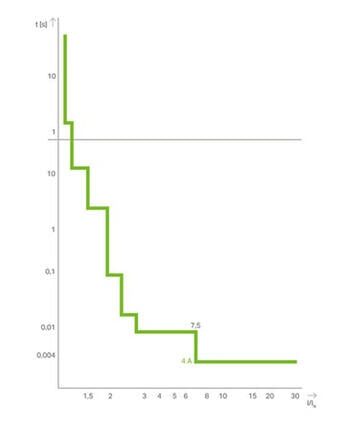
The ECB verifies that the output current is greater than the nominal current. As soon as the output current exceeds the nominal current, the output is electronically switched off by a semiconductor switch. The trip time depends on the magnitude of the overcurrent. The measurement of the output current, processing and calculation of the tripping time, as well as actuation of the semiconductor switch are performed by a microprocessor that monitors one or more output channels. The corresponding tripping times can be taken from the graph on the left.
Communication
Communication 1.0
Digital signaling (S/P)
- Remote digital input resets all tripped channels
- Digital output transmits a simple group message indicating whether one of the channels was tripped by an overcurrent
Build innovative machines faster without costly prototyping with Efficient Motion Control.
With Effective Motion Control, machine builders can easily overcome major challenges and enable faster time-to-market, increased functionality, resolve complex system requirements, and demands for safety and sustainability.



